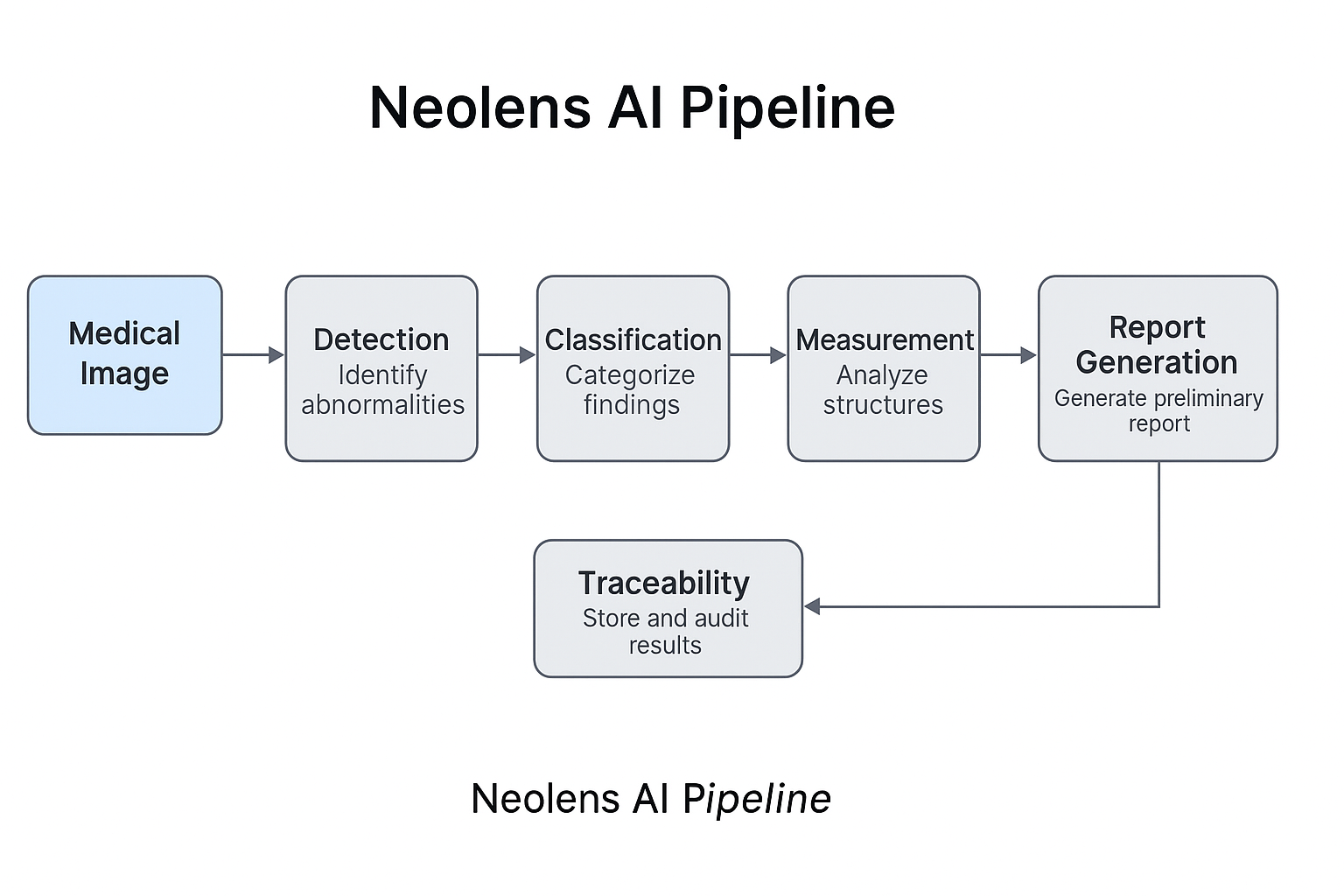
Anomaly Detection Module
The Detection module automatically identifies suspicious regions in medical images, such as X-rays or CT scans.
🎯 Purpose
This module flags potential abnormalities to support radiologists in prioritizing cases and reducing oversight.
🧩 How It Works
- Uses state-of-the-art computer vision techniques to scan images.
- Applies convolutional neural networks (CNNs) trained on labeled datasets.
- Outputs bounding boxes and heatmaps highlighting areas of interest.
⚙️ Key Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
sensitivity | float | Controls detection threshold, 0.0 (low) to 1.0 (high) | 0.75 |
image_modality | string | Type of input image: xray, ct, mri | xray |
min_area | int | Minimum size in pixels for detected anomalies | 50 |
tip
- Adjust sensitivity to balance false positives vs false negatives.
- Higher sensitivity catches more anomalies but increases noise.
📦 Output Format
Detection results include:
bounding_boxes: List of rectangles around suspicious areas.heatmaps: Optional overlay images highlighting regions.confidence_scores: Probability estimates per detected anomaly.
{
"detections": [
{
"bounding_box": [120, 80, 240, 160],
"confidence_score": 0.92,
"type": "nodule"
}
]
}
🛠️ Usage Example
curl -X POST "https://api.neolens.ai/v1/detection" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API_KEY>" \
-F "image=@chest_xray.png" \
-F "sensitivity=0.85"
🚩 Limitations
- May miss very small or subtle anomalies.
- False positives possible in noisy images.
- Performance varies by image modality and quality.